The War of 1812: Naval Battles and Their Impact
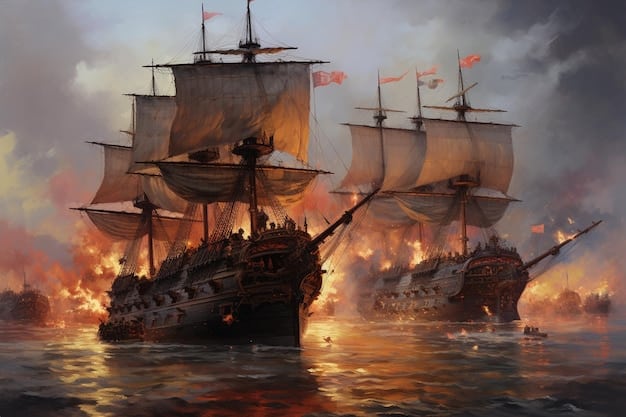

The War of 1812, often overshadowed in historical narratives, was significantly shaped by naval engagements, which played a crucial role in defining the conflict’s outcome and establishing maritime power dynamics.
Dive into the War of 1812: Exploring the Naval Engagements That Defined the Conflict, a crucial period where maritime battles determined the fate of nations and shaped the future of naval warfare.
The War of 1812: A Naval Overview
The War of 1812, fought between the United States and Great Britain, was significantly influenced by naval conflicts. Control of the seas was vital for both sides, impacting trade, supply lines, and overall military strategy.
This conflict saw a young American navy challenge the established might of the Royal Navy. The outcomes of key naval battles would shape the trajectory of the war and its lasting consequences.
Key Naval Objectives
For the United States, the primary naval objective was to disrupt British trade and assert maritime rights. For Great Britain, it was to blockade American ports and prevent American ships from interfering with British interests.
The State of the Navies
The Royal Navy was the largest and most experienced in the world, while the U.S. Navy was relatively small and untested. Despite being outnumbered, American ships were often better designed and manned by skilled sailors.
- American frigates like the USS Constitution and USS United States were heavily armed and proved surprisingly effective.
- The British attempted to enforce a strict blockade, which had a significant impact on the American economy.
- Both sides employed privateers, privately owned ships authorized to attack enemy vessels.
Understanding the initial objectives and the state of the navies provides a foundation for examining the specific naval engagements that defined the War of 1812.

Early American Naval Victories
The early stages of the War of 1812 saw a series of surprising victories for the U.S. Navy. These victories boosted American morale and challenged the perceived invincibility of the Royal Navy.
These engagements demonstrated the design and skill of American ships and sailors, shifting the narrative of the war and forcing the British to reassess their strategy.
USS Constitution vs. HMS Guerriere
One of the most famous early victories was the battle between the USS Constitution and the HMS Guerriere. The Constitution, nicknamed “Old Ironsides,” decisively defeated and destroyed the Guerriere.
USS United States vs. HMS Macedonian
Another significant victory occurred when the USS United States captured the HMS Macedonian. This victory further highlighted the capabilities of the American navy.
- These victories were largely due to superior gunnery and ship design.
- The American public celebrated these victories, boosting morale and national pride.
- The British were shocked by these defeats and began to take the American navy more seriously.
These early victories established the U.S. Navy as a force to be reckoned with, changing the dynamics of the war and setting the stage for future naval engagements.
The British Blockade and its Impact
Despite early American naval victories, the British Royal Navy’s extensive blockade of American ports had a profound impact on the United States. This blockade hampered American trade, crippled the economy, and put pressure on the American government.
The blockade was a strategic response by the British to neutralize American naval successes and exert economic control. Its effects were widespread and long-lasting.
Effects on American Trade
The blockade severely restricted American trade, preventing ships from entering or leaving ports. This led to a sharp decline in exports and imports, causing economic hardship for merchants and farmers.
Impact on the American Economy
The economic consequences of the blockade were significant, leading to inflation, unemployment, and financial instability. The government struggled to finance the war effort due to reduced customs revenue.
The effectiveness of the British blockade underscored the importance of naval dominance and the vulnerability of a nation dependent on maritime trade.
- The blockade highlighted the need for a stronger American navy and coastal defenses.
- American privateers attempted to evade the blockade, but their efforts were limited.
- The economic hardship caused by the blockade contributed to growing dissent against the war in some regions.
The British blockade significantly influenced the course of the war, demonstrating the strategic importance of naval power and its impact on a nation’s economy and morale.
Battles on the Great Lakes
Control of the Great Lakes was strategically vital during the War of 1812, as these waterways served as crucial transportation routes for troops and supplies. Naval battles on the Great Lakes determined control of the region and influenced the outcome of land campaigns.
The battles on these inland seas were characterized by intense fighting in confined spaces, directly impacting the war’s progress in the northern theater.
The Battle of Lake Erie
The Battle of Lake Erie in 1813 was a decisive victory for the American fleet under the command of Oliver Hazard Perry. This victory gave the United States control of Lake Erie and allowed for the recapture of Detroit.
The Battle of Lake Champlain
The Battle of Lake Champlain in 1814 saw another crucial American naval victory, preventing a British invasion from Canada. This battle secured the northern border of the United States.
- The construction and deployment of warships on the Great Lakes posed significant logistical challenges.
- These naval victories were crucial in preventing British control of the Great Lakes region.
- Oliver Hazard Perry’s famous quote, “We have met the enemy and they are ours,” became a symbol of American resolve.
Naval engagements on the Great Lakes were pivotal in determining the balance of power in the northern theater of the War of 1812, securing vital transportation routes and thwarting British invasion attempts.
Privateering and Commerce Raiding
Privateering played a significant role in the War of 1812. Both the United States and Great Britain authorized privateers to attack enemy merchant ships, disrupting trade and contributing to the overall naval effort.
These privately owned warships often operated with considerable success, adding another dimension to the naval conflict and impacting the economies of both nations.
The Role of American Privateers
American privateers targeted British merchant ships, capturing valuable cargo and disrupting British trade routes. They operated throughout the Atlantic, Caribbean, and even in British waters.
Impact on British Commerce
The activities of American privateers caused significant losses for British merchants and insurers. They forced the British to divert naval resources to protect their merchant fleet.
Privateering offered opportunities for profit and adventure, attracting sailors and investors and becoming a significant aspect of the war effort.
- Privateers were a cost-effective way to supplement naval power.
- The threat of privateers increased insurance rates and shipping costs for British merchants.
- Some American privateers became famous for their daring exploits and successful captures.
Privateering in the War of 1812 disrupted commerce, strained naval resources, and added a layer of economic warfare to the overall conflict.
The End of the War and its Naval Legacy
The War of 1812 ended with the Treaty of Ghent in 1814, which restored pre-war boundaries. While the treaty addressed some of the issues that led to the war, the naval engagements had a lasting impact on both the United States and Great Britain.
The naval aspects of the war reshaped maritime strategies and strengthened the position of the U.S. Navy on the global stage.
Naval Lessons Learned
The war highlighted the importance of a strong navy for protecting national interests and securing trade routes. Both sides learned valuable lessons about naval warfare, ship design, and strategic deployment.
Strengthening of the U.S. Navy
The War of 1812 led to a significant expansion and modernization of the U.S. Navy. The performance of American ships in the war demonstrated the need for a professional and well-equipped naval force.
- The war fostered a sense of national pride and confidence in the U.S. Navy.
- The war contributed to the development of new naval technologies and tactics.
- The War of 1812 marked a turning point in the evolution of the U.S. Navy, establishing it as a credible force on the world stage.
The War of 1812 left a lasting naval legacy, emphasizing the significance of maritime power and shaping the future development of naval forces in both the United States and Great Britain.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| ⚓ Naval Objectives | US aimed to disrupt British trade; Britain sought to blockade US ports. |
| 🚢 Early Victories | USS Constitution and USS United States secured key wins, boosting US morale. |
| 🌊 British Blockade | Severely impacted American trade and economy, causing widespread hardship. |
| ⚔️ Great Lakes Battles | US victories on Lake Erie and Lake Champlain secured vital transportation routes. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
The primary causes included British impressment of American sailors, trade restrictions imposed by Britain, and American expansionist desires in British territories.
▼
During its battle with HMS Guerriere, cannonballs appeared to bounce off its hull, leading a crew member to exclaim that its sides were made of iron.
▼
It secured American control of Lake Erie, allowing for the recapture of Detroit and facilitating further military operations in the Great Lakes region.
▼
American privateers disrupted British trade, caused significant losses for merchants, and forced Britain to divert naval resources to protect their ships.
▼
The war ended with the Treaty of Ghent, restoring pre-war boundaries. It led to increased American nationalism and a stronger U.S. Navy.
Conclusion
The naval engagements of the War of 1812 were crucial in shaping the conflict’s outcome and its lasting impact. From the early American victories at sea to the strategic battles on the Great Lakes and the disruptive actions of privateers, each naval aspect played a vital role in defining the war’s narrative and solidifying the United States’ position as a maritime power.





